This case explores making a precise implant restoration surgical guide thanks to 3D scanning and 3D printing. Read on to find out more about this digital dentistry workflow.
Introduction
Traditional dental implants primarily rely on the dentist’s experience to evaluate the success rate of the implant. Because there is no way to determine the position of implant placement through CT examination directly, it is necessary to cut tissue during the operation and estimate the implant placement based on the dentist’s sensory experience. Yet the oral situation of each patient is different. The depth, direction and accuracy of the implant position cannot be fully realized by naked eyes and experience alone.
A precise implant restoration surgical guide can assist dentists in accurately positioning implant placement. They clarify the implant depth and angle of the implant and avoid facial blood vessels, important nerves, etc., to ensure implant safety and accurate occlusion. These digital guides can also leverage a patient’s bone mass to provide optimal support for the implant, avoiding potentially weak areas that may compromise the restoration.
The following is a case of using SHINING 3D’s Digital Surgical Guide solution to complete precise implant work. The dentist used SHINING 3D’s latest intraoral scanner Aoralscan 3 to scan directly in the patient’s mouth and design the implant surgical guide based on the scan data. This data was then sent to SHINING 3D’s AccuFab-D1s 3D printer to print out and complete the precise implant.
Patient information
This patient is a 25-year-old woman with fixed appliances on the upper and lower jaws. #37 has implant anchors at the distal free end. #36 is missing, which reduces the chewing efficiency. She now requires repair.
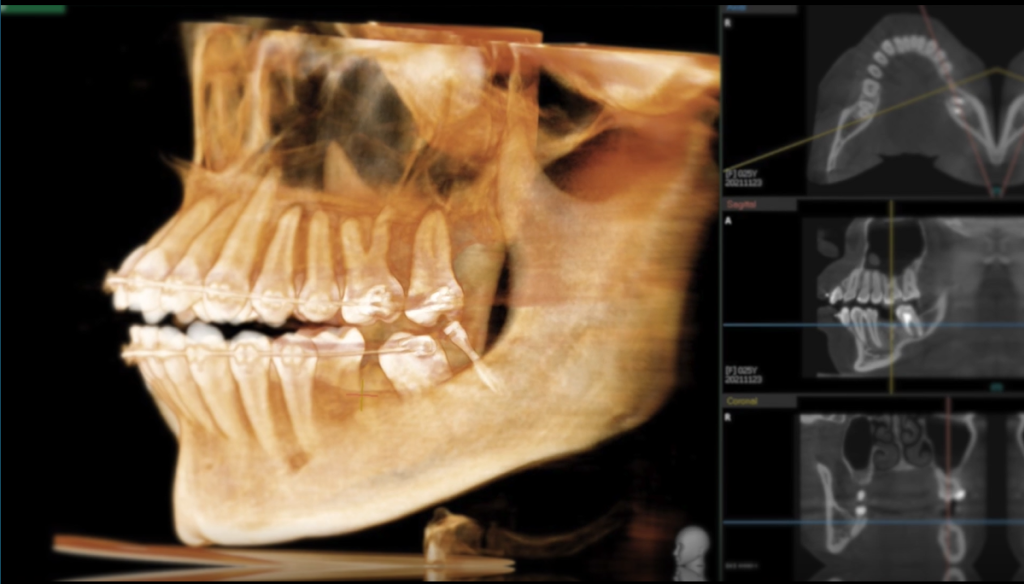
The patient’s preoperative CT showed the bone condition was still good. Hence, the digital guide is followed throughout the whole implant restoration process. The implant is set in place at one time, which greatly reduces the patient’s discomfort.
3D scanning
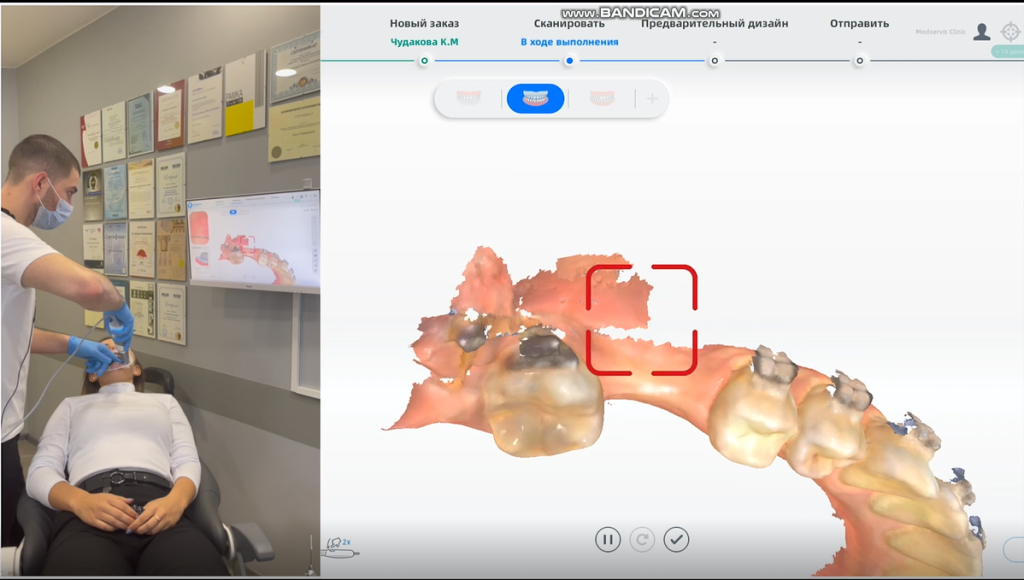
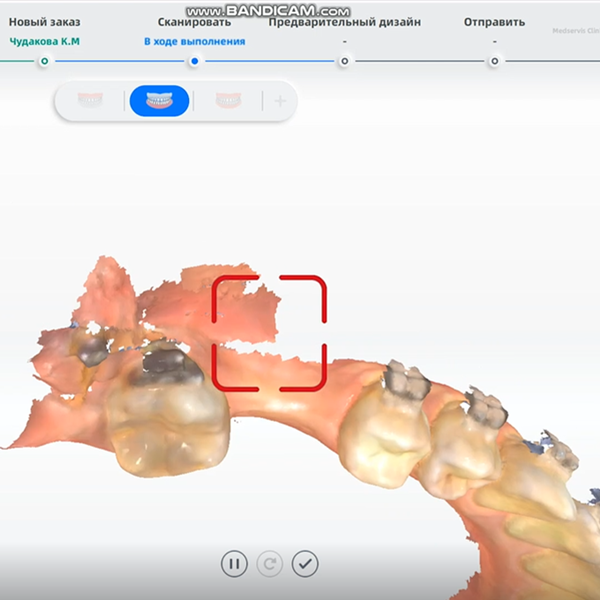
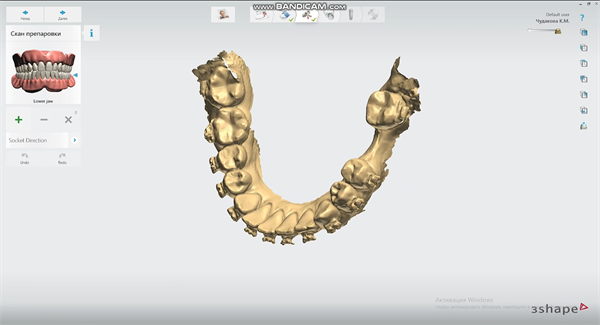
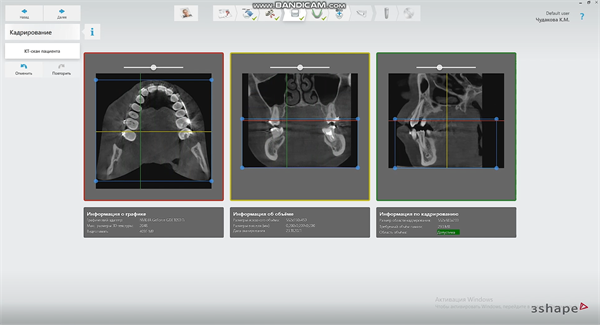
We use the Aoralscan 3 to directly scan the arch where the patient needs implants. The patient wears braces, and these must also be clearly scanned by the system. Thanks to the “true color” and high precision of the Aoralscan 3, the dentist can check which areas have not been scanned clearly and which areas need to be added in real time. The patient can also check the real-time status of her mouth, so she can better understand the dentist’s treatment plan, and finally get accurate digital working arch data (including braces).
Precise implant restoration surgical guide design
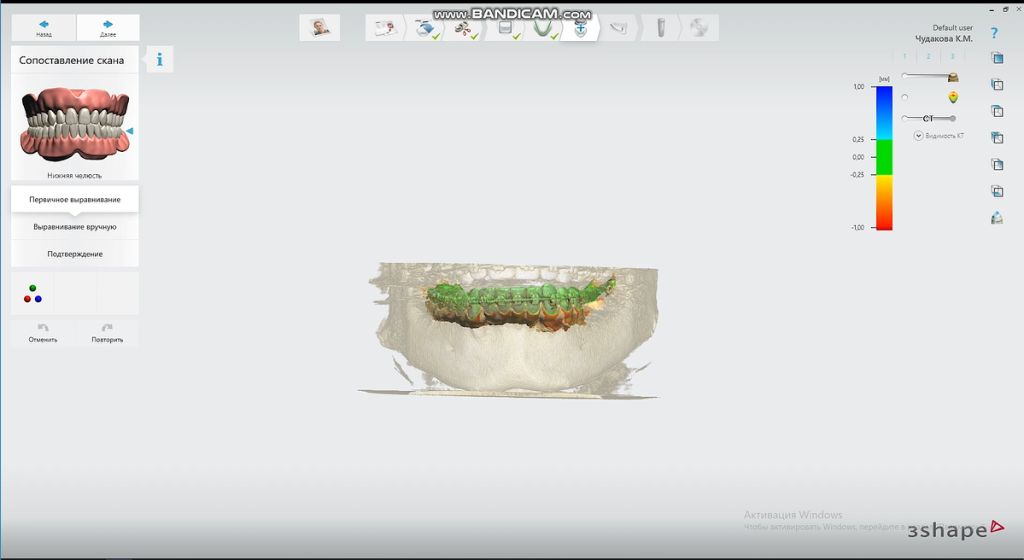
We import the scanned data into the guide design software and align the CT data for subsequent guide design.
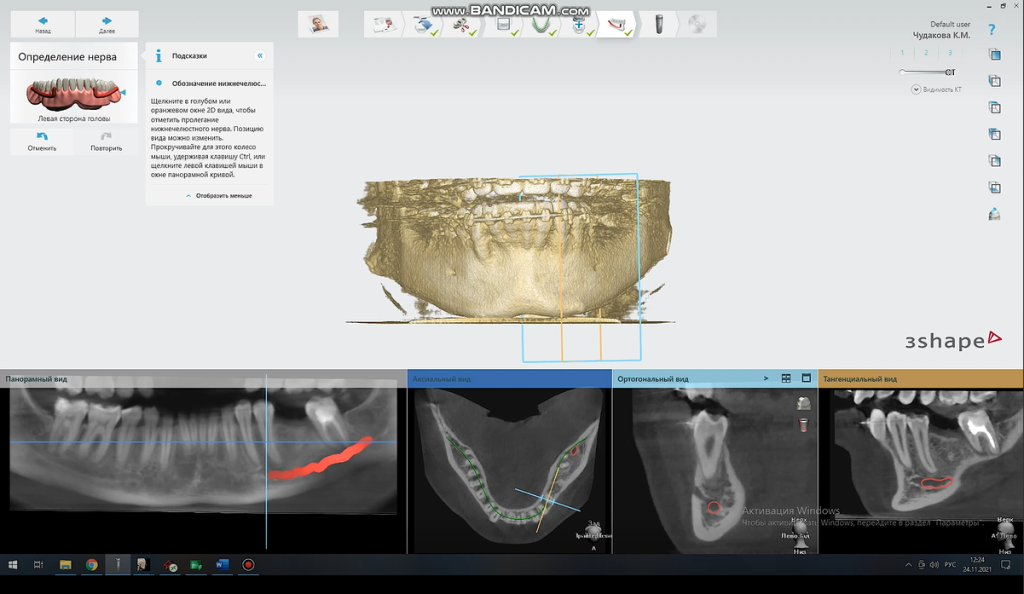
We carry out the neural tube modeling in the implant area as a reference to avoid the implant from damaging the nerve during insertion.
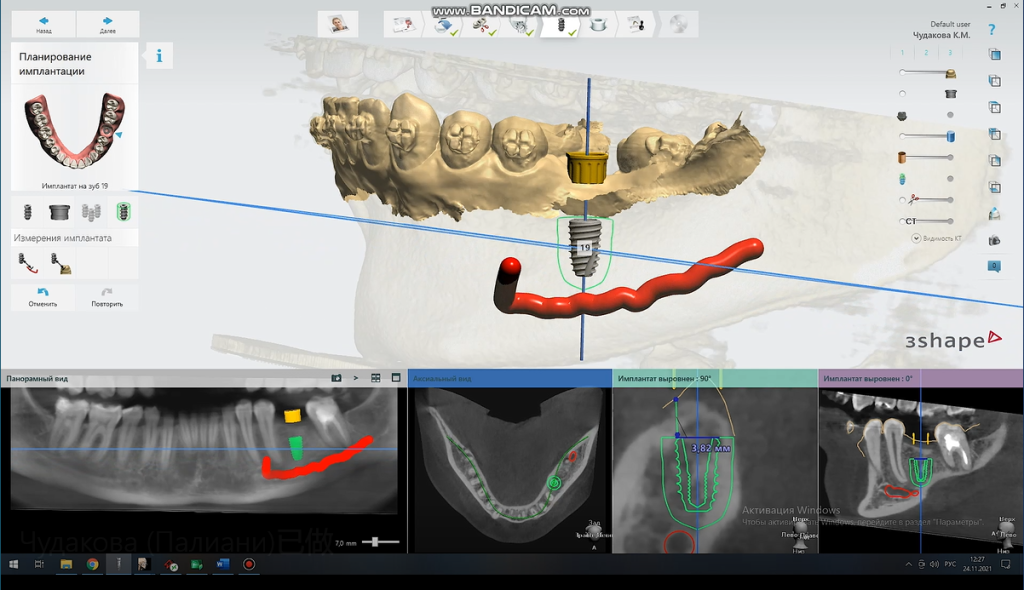
Choose the appropriate brand and model of the implant. Design the direction, position, angle, and depth of the implant to ensure the implant’s success and long-term stability.
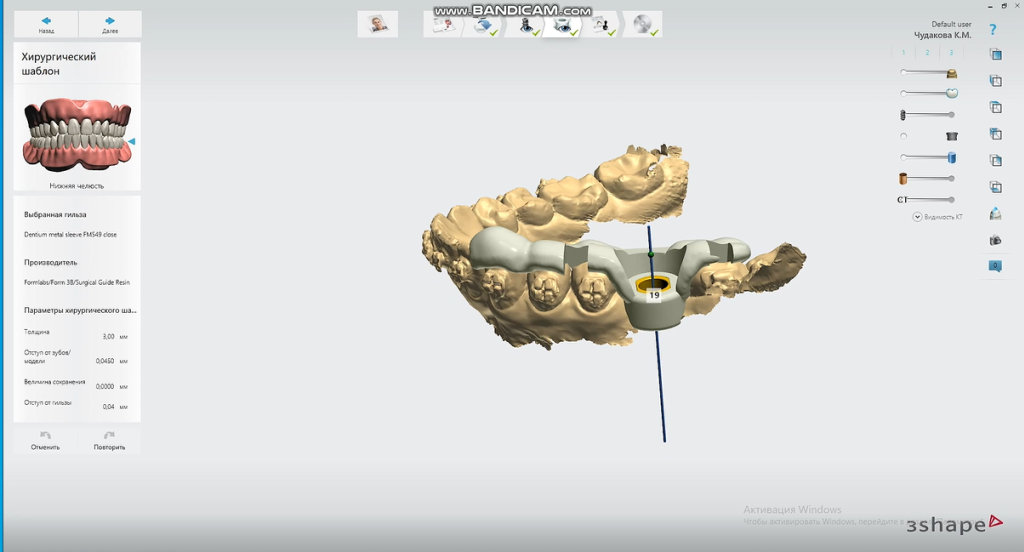
The software generates the guide plate once the user confirms the planting plan.
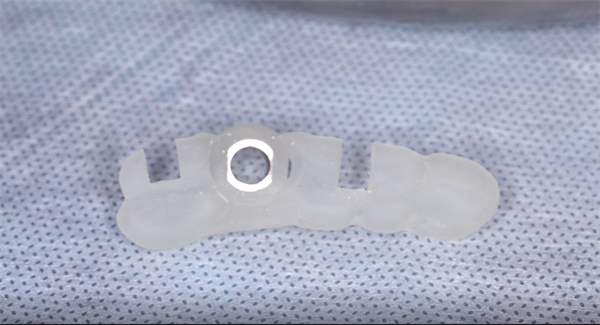
3D printing the precise implant restoration surgical guide
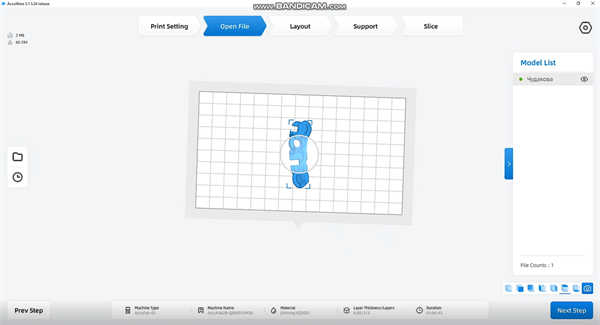
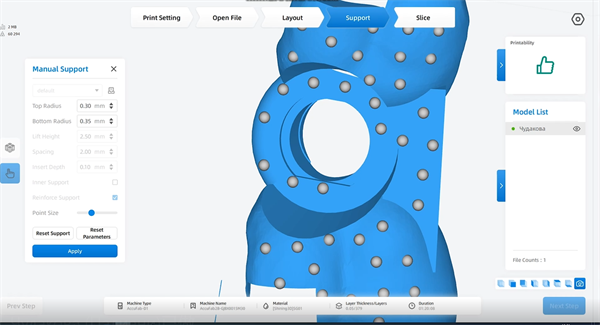
Import the designed guide plate into the slicing software. Adjust the printing position, edit the support (especially the support where the sleeve is located), and then slice.
Import the sliced file into the printer for direct printing. Then perform post-processing on the print, sterilize, and bring the sleeve to prepare for the next operation. Thanks to the high precision of the AccuFab-D1s, the sleeve can be accurately positioned.
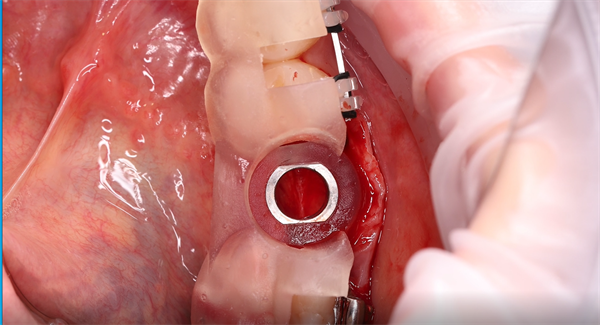
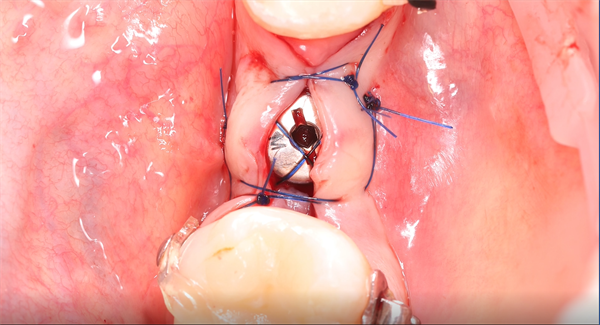
Fix the guide plate and use drill needles of different diameters to prepare the cavity with the guide plate’s guidance. Finally, implant the corresponding implant and suture to complete the operation.
Final result
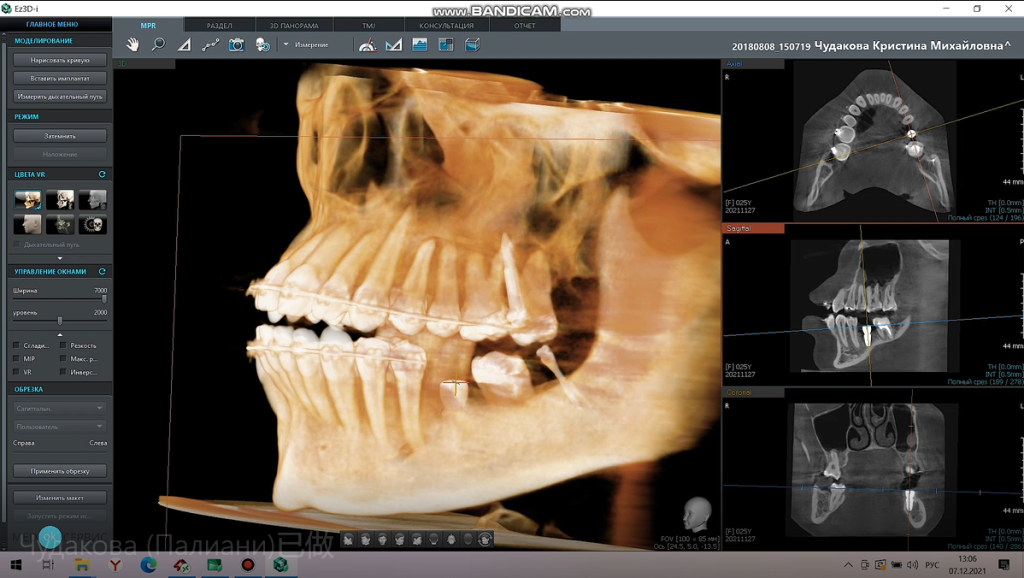
The postoperative CT showed that the implant was accurately implanted in the corresponding position in accordance with the pre-determined plan.
 ENG
ENG