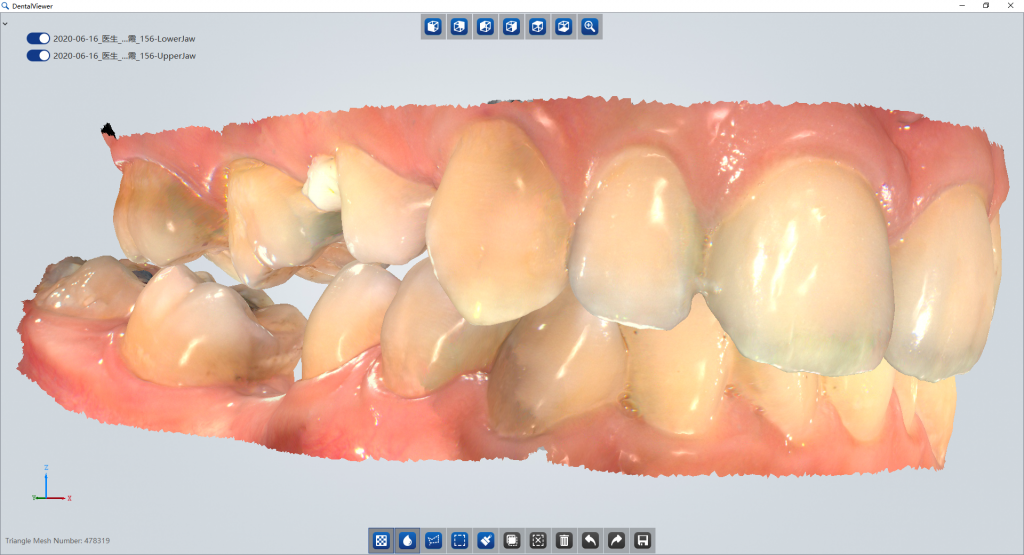
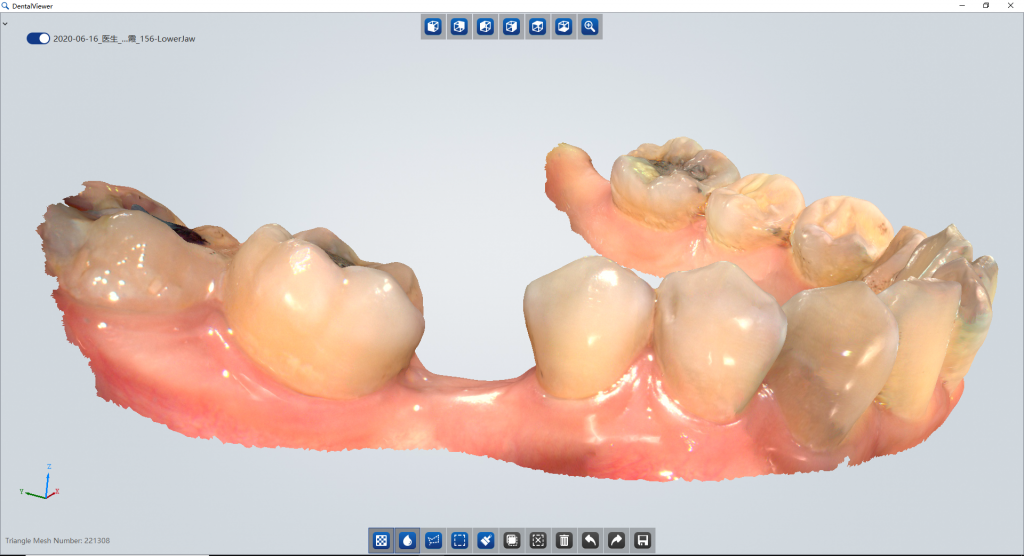
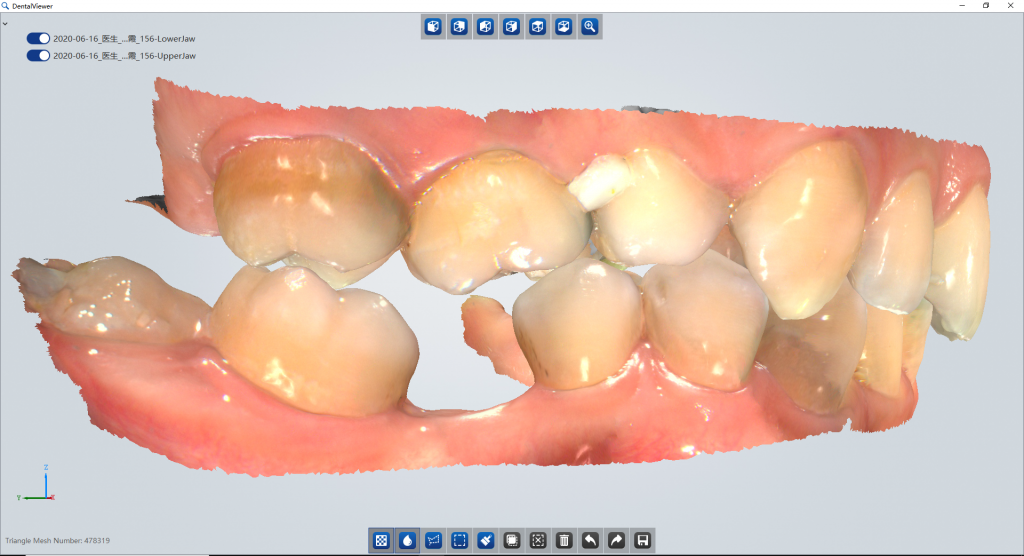
A team of dentists at Shenzhen University Hospital performed implantology between narrow posterior teeth with digital dentistry techniques.
Dentists
The dentists that carried out this case at Shenzhen University Hospital are:
- Deng Yongqiang, Director of stomatology department at Shenzhen University Hospital
- Li Xin, Post Doctor at HKU Faculty of Dentistry
- Li Xuguang, graduated from West China School of Stomatology, Sichuan University
Patient information
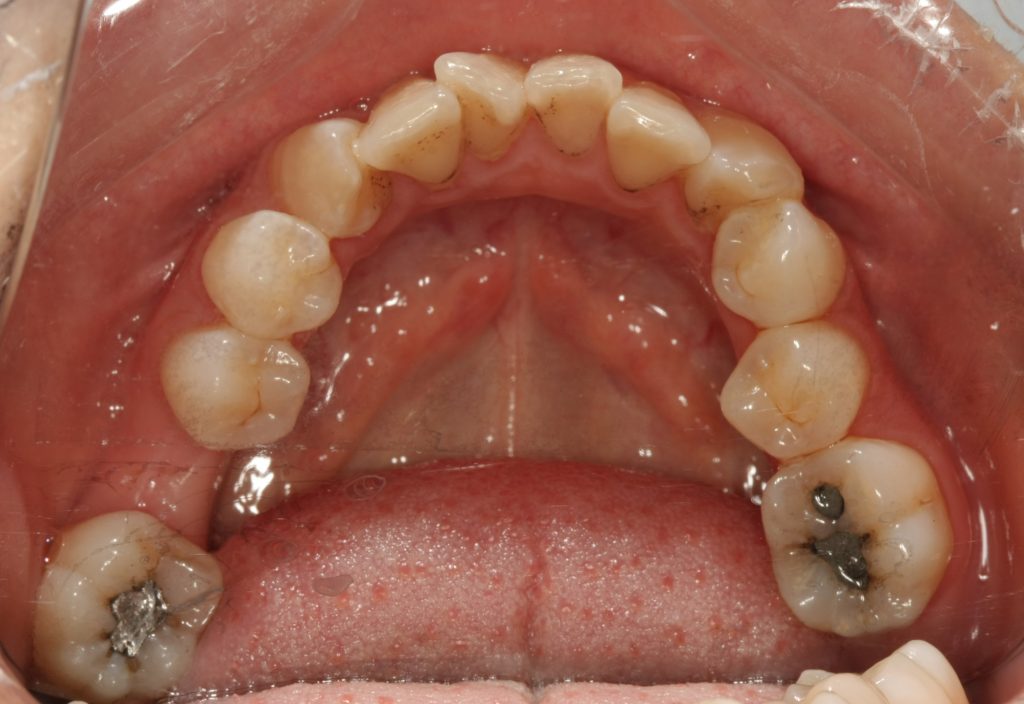
Patient: Female, 26 years old
Complaint: Right lower posterior tooth was missing for a year
Medical History: The patient reported no history of hypertension, heart disease, diabetes, myositis, tuberculosis, or other infectious diseases. No history of major trauma or surgery, no history of drug, allergy, or blood transfusion either.
Physical examination: #46 was missing, alveolar ridge shape was blade-like, and mucosal color and morphology were normal. The width of the alveolar ridge was about 2mm and the gap in the missing area was acceptable. #47 was inclined to the middle and loose (-).
Auxiliary examination: CBCT showed that the alveolar bone in the tooth-missing area was general. The distance between the top of the alveolar ridge and the inferior alveolar neural tube is 19.89mm. No periapical lesions were observed in the adjacent teeth and no abnormal lesions were observed in the alveolar bone either.
Diagnosis: Missing tooth
Treatment plan: #46 implant-based restoration.
Preoperative CT
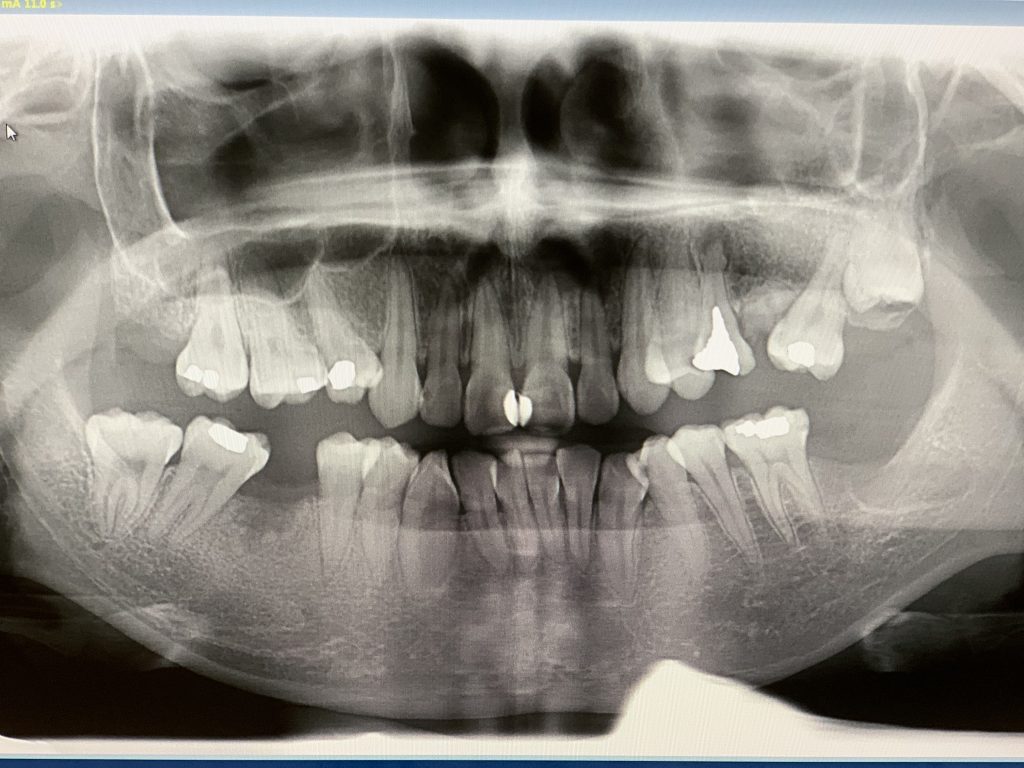
Panoramic X-ray 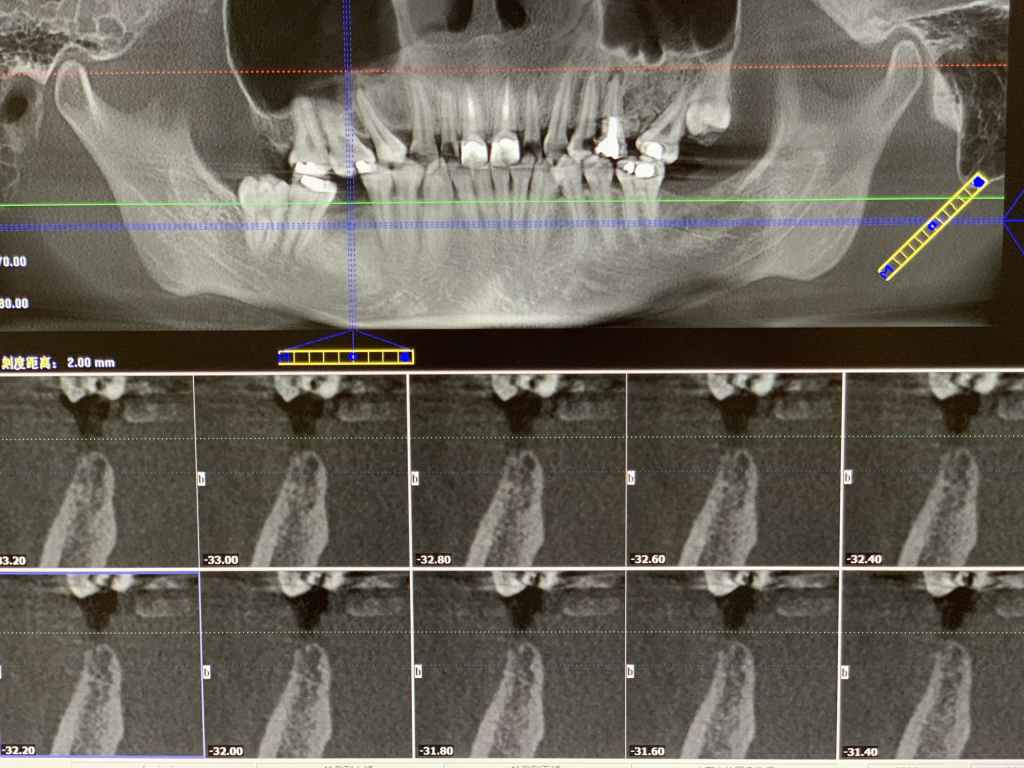
Implant bed region
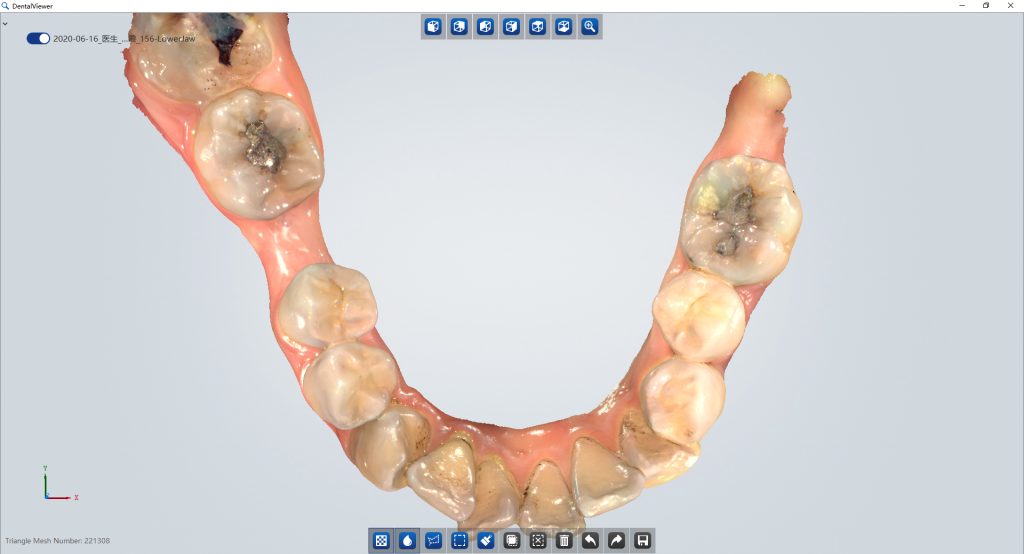
Intraoral Scanning
Scan the patient with Aoralscan intraoral scanner. The Aoralscan features true color acquisition, easy operation, intelligent scan algorithms, and motion sensing. Dentists can get the digital impression very easily under excellent infection control.
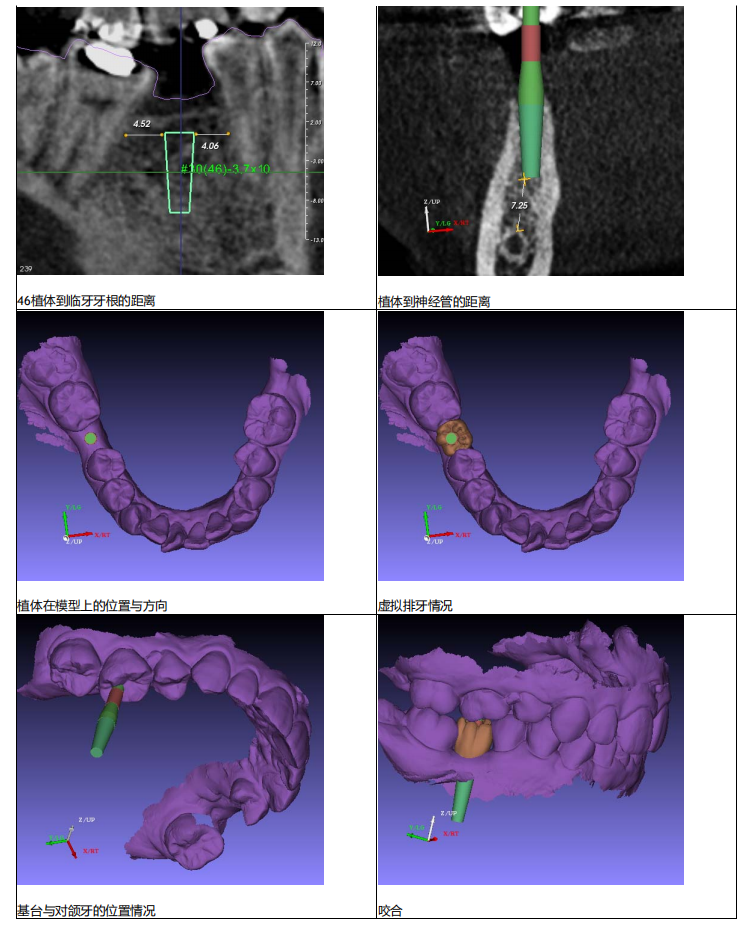
Operation plan
- Tooth position : 30 (FDI #46)
- Diameter of implant : 3.70
- End diameter of the implant : 2.50
- Length of the implant : 11.50
- Depth of the preparation : 20
- Elongation of drilling : 8.5
- Tissue ring cutting :3.70
- Sinus lift :0.00
- Handle: D2.0 L20.00
.png)
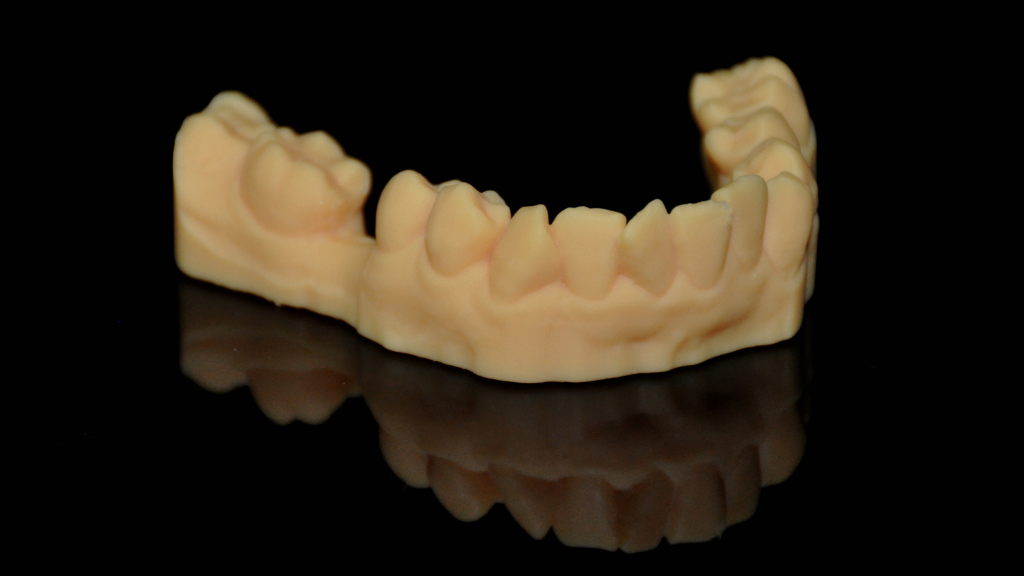
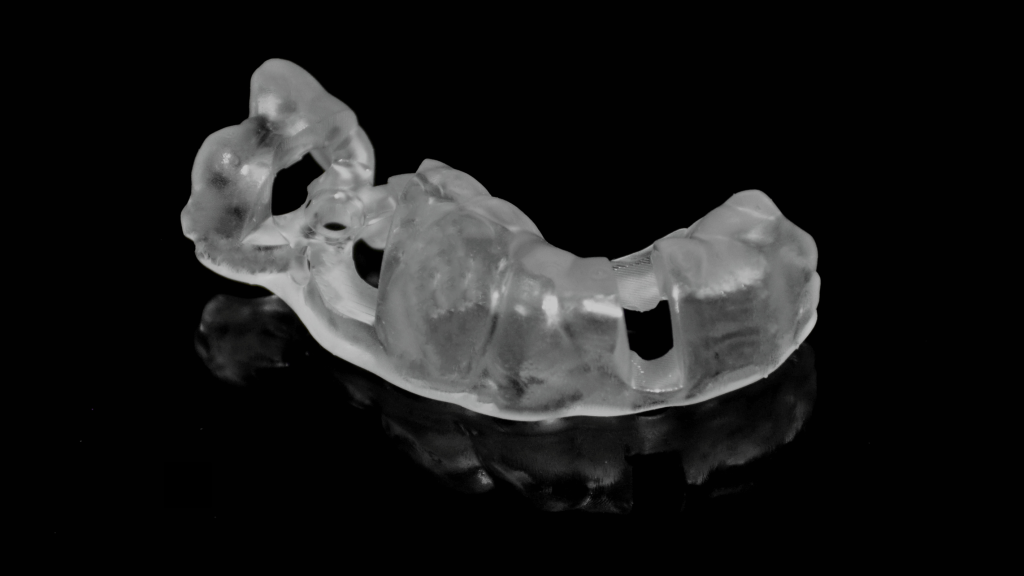
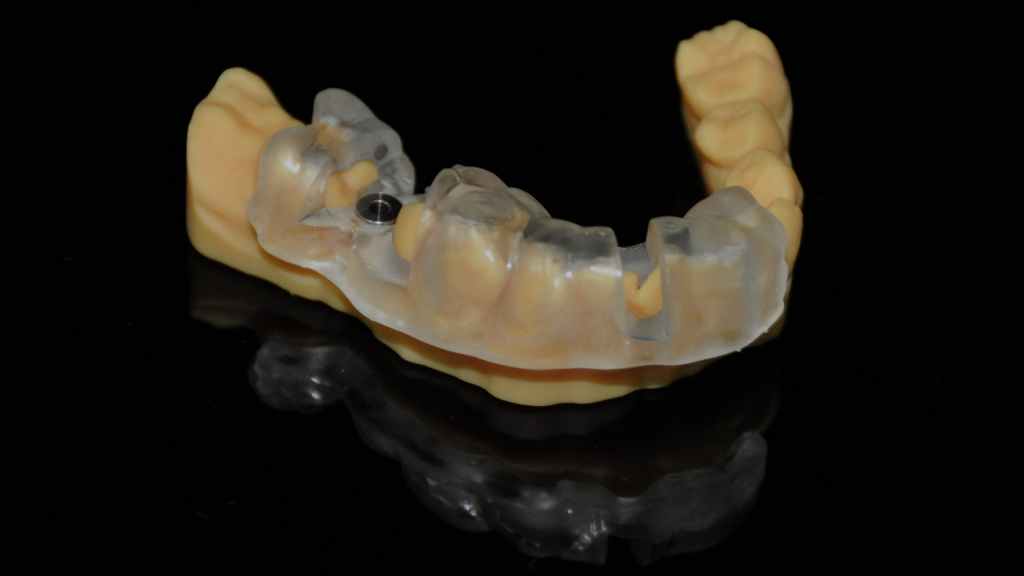
Print Implant Model and Surgical Guide
Then, print the implant model and surgical guide with AccuFab-D1 dental printer. The AccuFab-D1 supports support automatic creation and one-click printing, offering users very intuitive and user-friendly print experience.
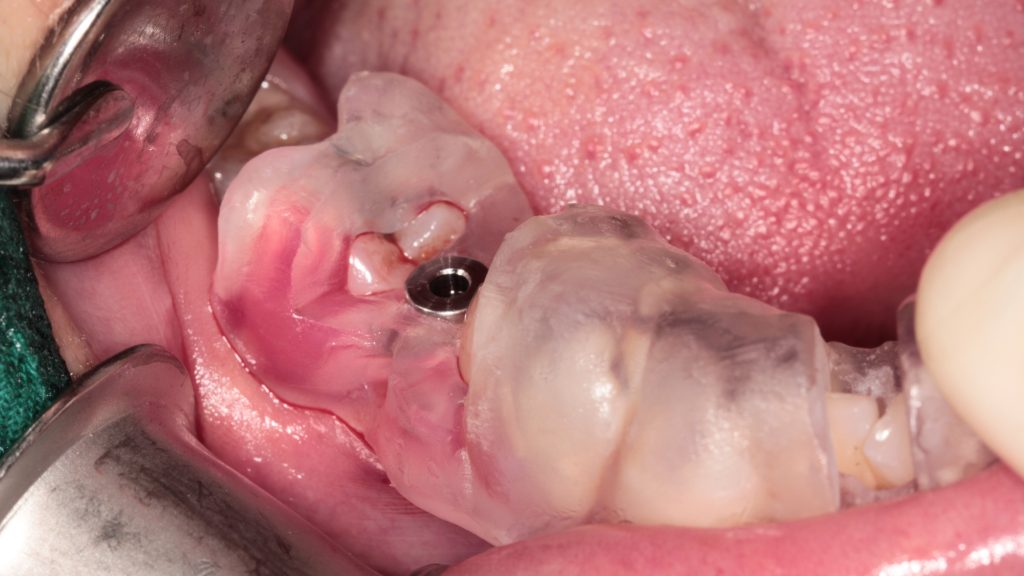
The surgical guide is perfectly fit with the implant model.

Implant Surgery
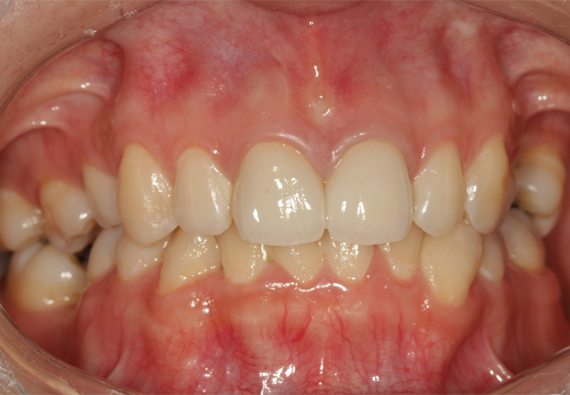
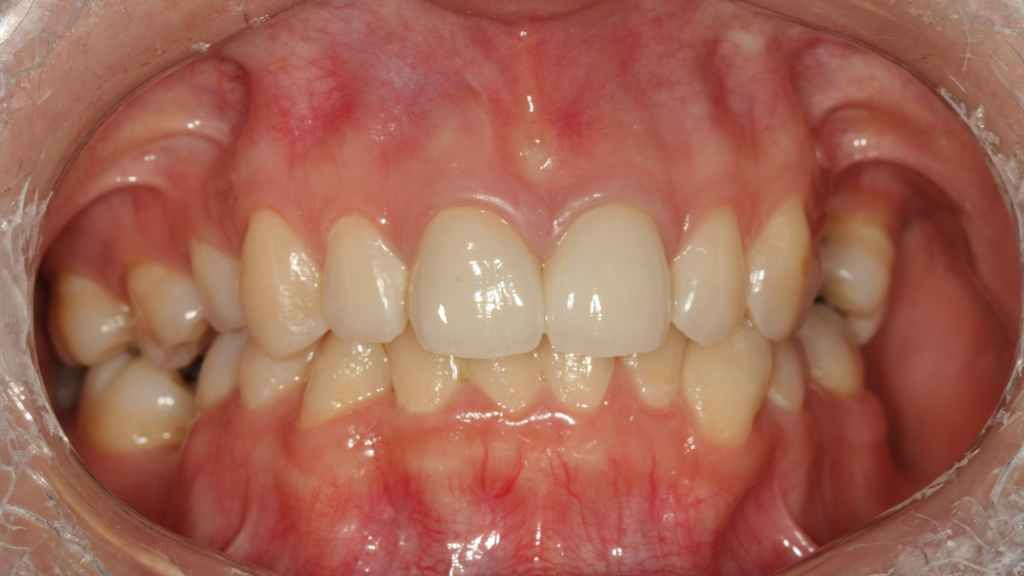
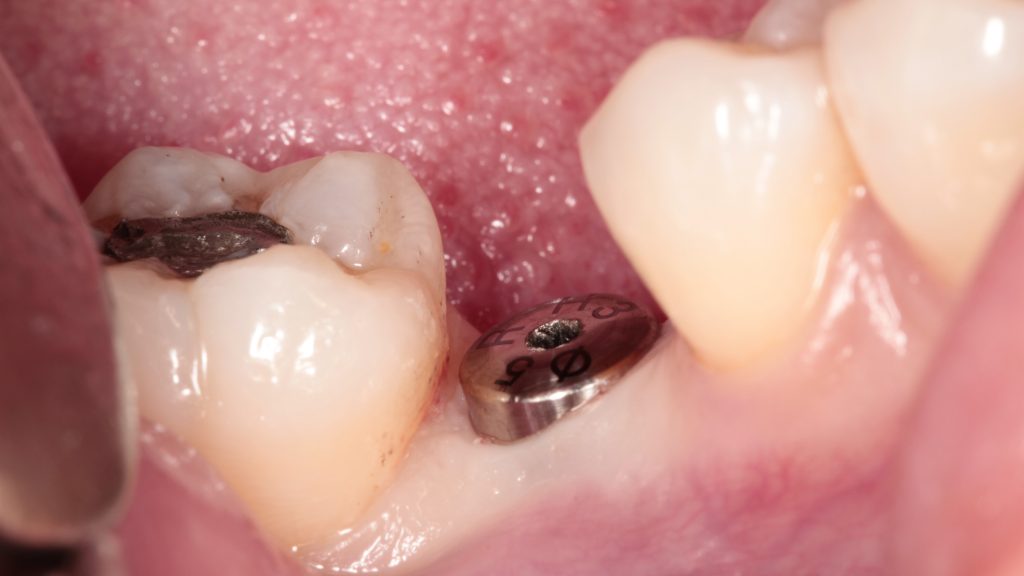
Preoperative intraoral view
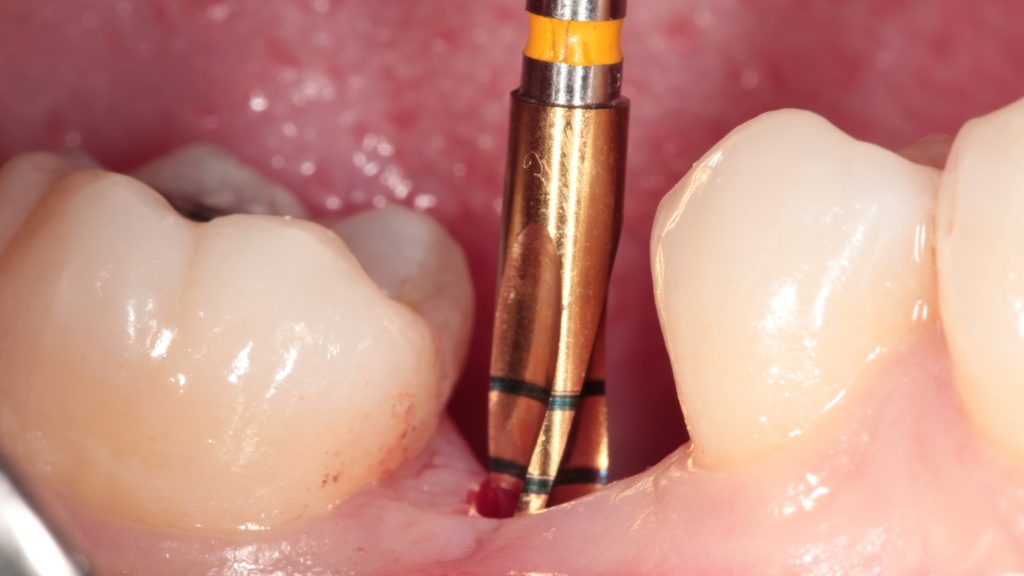
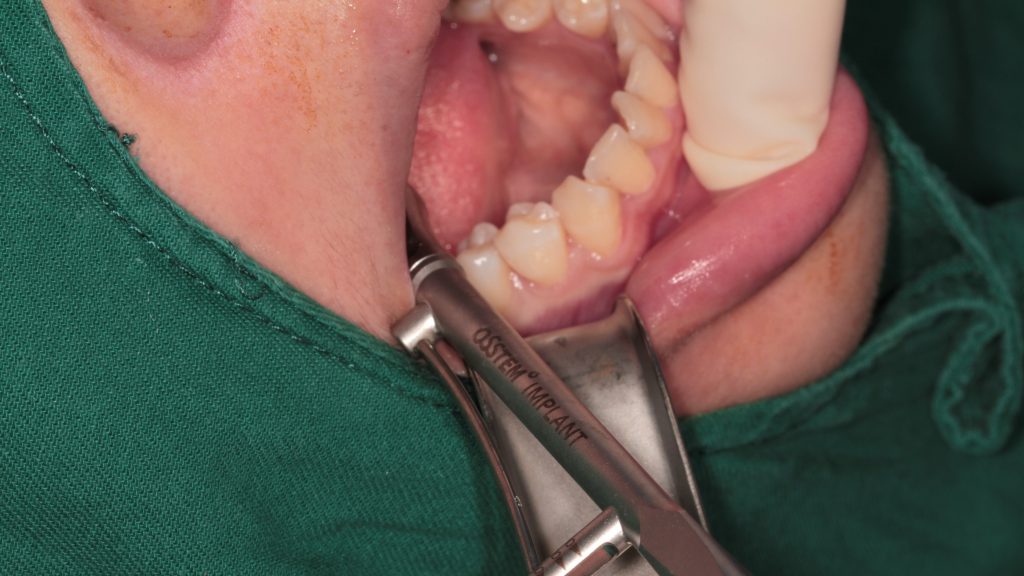
Insert guide in place and prepare implant bed with pilot drill. Check the depth and orientation of the implant bed after drilling.
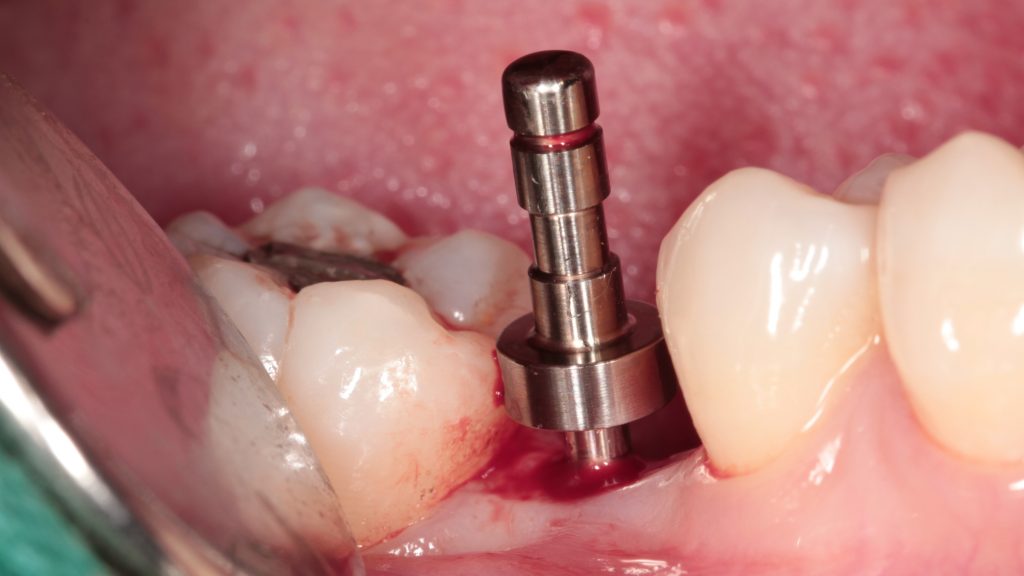
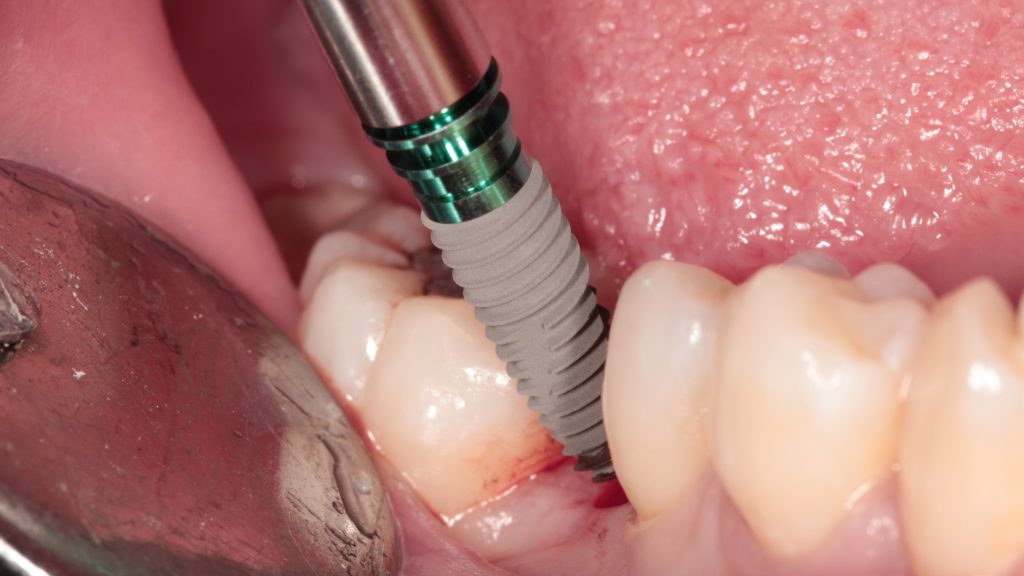
Finish drilling and place implant.
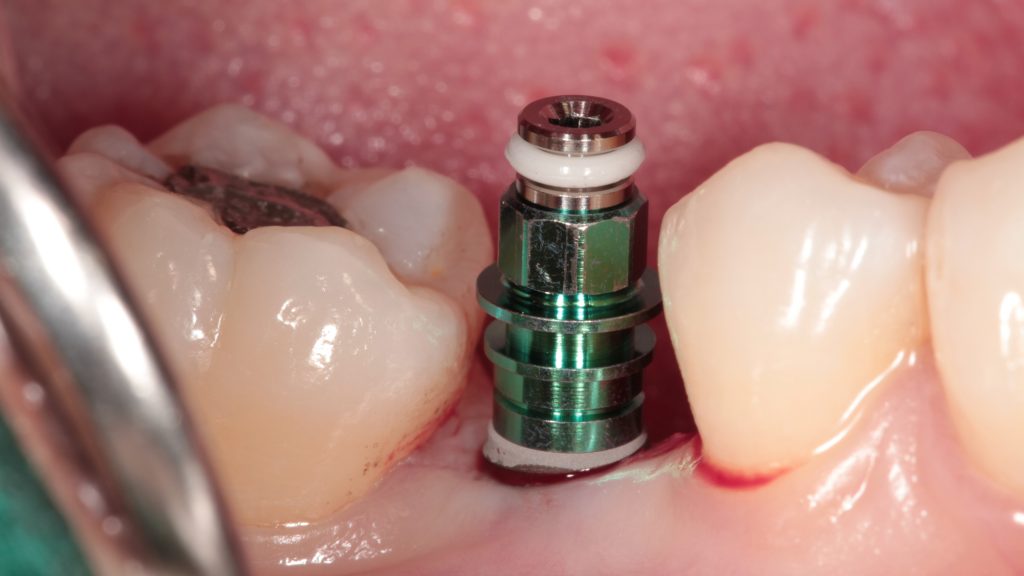
Tighten the implant with torque wrench
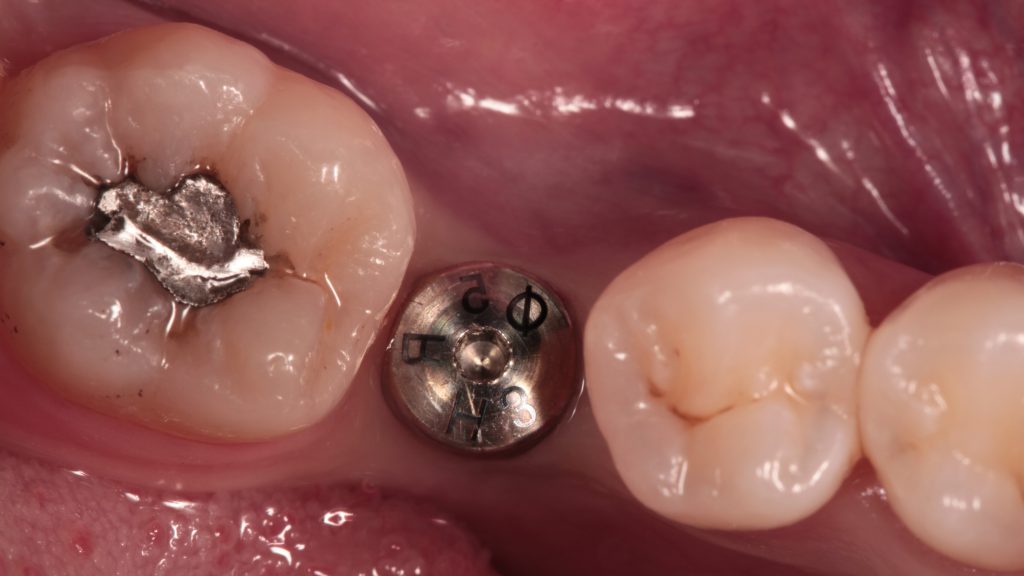
Place healing abutment and complete the surgery.
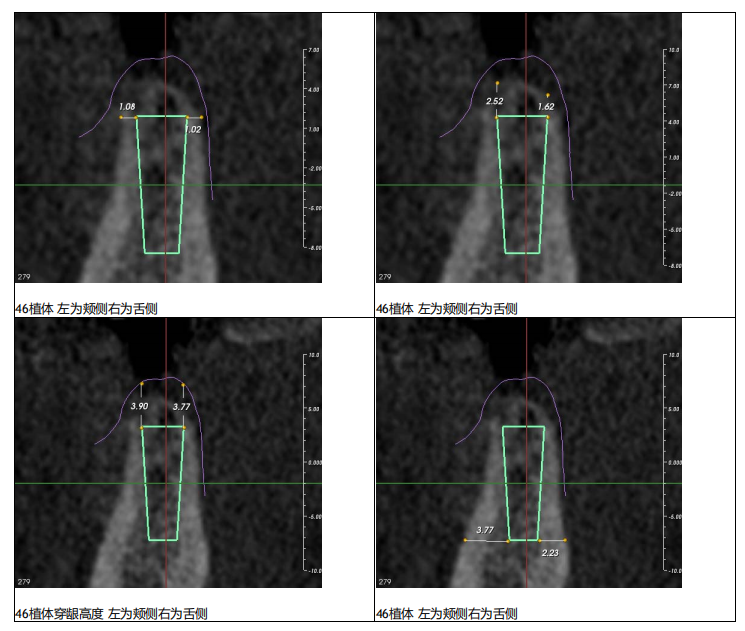
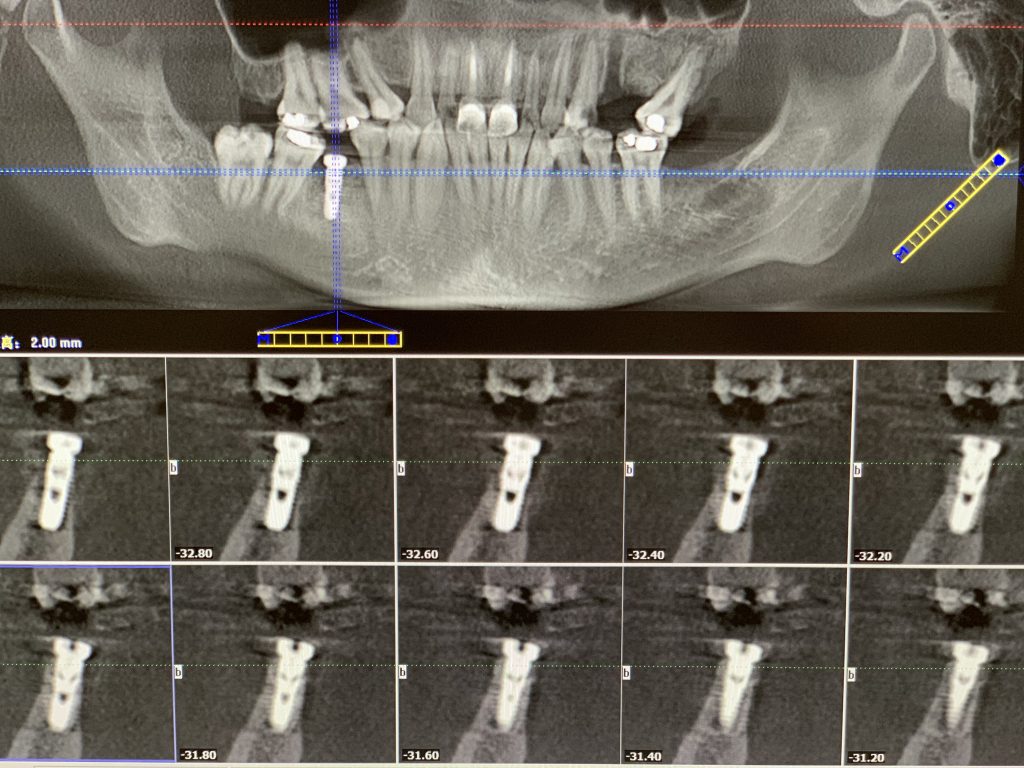
Postoperative CT:
Due to buccal and lingual bone absorption, and the superposition of narrow tooth space and other factors, manual implantation was not available. After using a pilot drill guide for hole preparation, the orientation and depth of the hole preparation can be clearly grasped in the subsequent reaming. This greatly improves the accuracy and safety of the operation.
 ENG
ENG